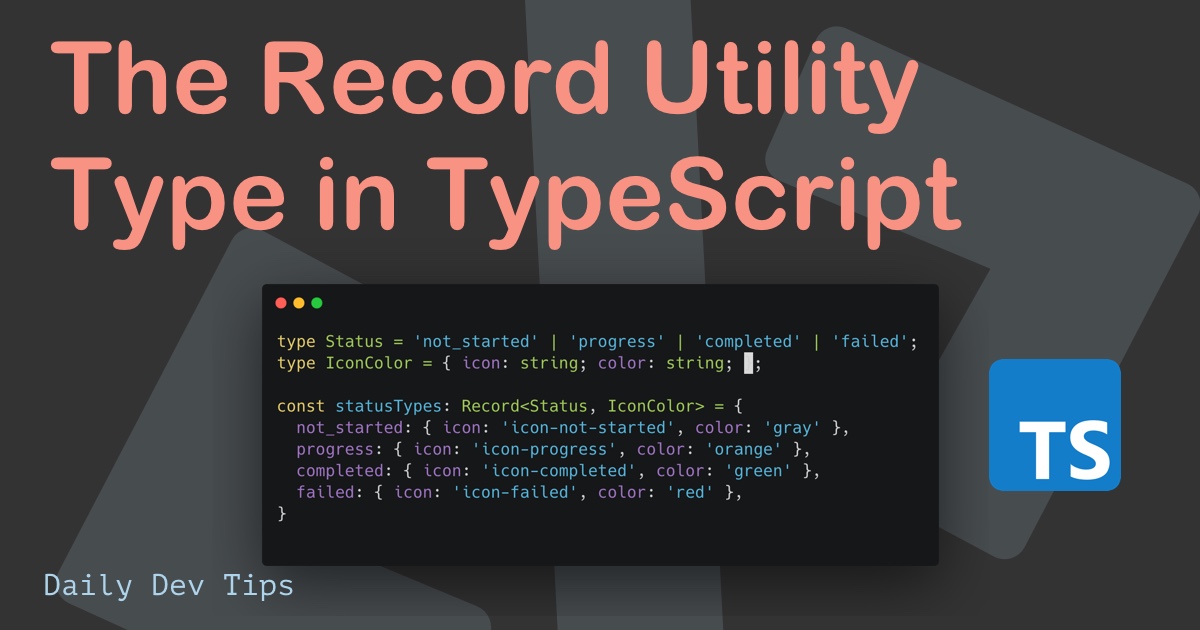
TypeScript comes with several utility types. These are utilities we can use to do type transformations.
This article will look at the Partial and Required types.
To give you a bit more context, you might have written an interface or type that reflects a user object, but in some cases, you want to use only specific fields or change which fields are required from this interface.
And that's precisely where the utility types come in handy, there is a whole set of them, and I'll be going through the most commonly used ones.
The TypeScript Partial utility type
Let's take the following example interface to work with.
interface User {
firstname: string;
lastname?: string;
age: number;
}As you can see, we made two fields required: firstname and age. The lastname field is optional because we added the ?.
However, what if we have an update where we would allow all of the fields to be optional and valid?
This could, for instance, be if we have a UI where each field will auto-update without knowing the other fields.
Our function for this could be updateUserField, which would accept any user fields.
const updateUserField = (id: number, fieldsToUpdate: Partial<User>) => {
return db.update(id, fieldsToUpdate);
};And we can now use this to update each field individually without needing the other ones to be set.
updateUserField(1, {
firstname: 'Chris',
});
updateUserField(1, {
age: 32,
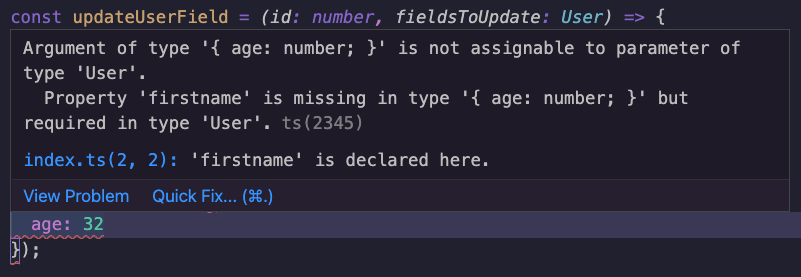
});This is now a valid code. However, if you would remove the Partial utility, you would see it throws some TypeScript errors about the missing fields.
The TypeScript Required utility type
On the other hand, there might be cases where you expect the value to be set.
Let's look at our user example again. By default, you might have an object where the ID is not required since we don't know it yet, but once the user is created, we could set it to be required.
interface User {
id?: number;
firstname: string;
lastname: string;
}We can use this User interface without specifying the ID when creating the user.
But when we want to update the user, we want to ensure the ID is set.
const updateUser = (user: Required<User>) => {
db.update(user);
};
updateUser({
id: 12,
firstname: 'Chris',
lastname: 'Bongers',
});Because of the Required type, every field in the User interface is now required.
A cool thing with TypeScript utility types is that you can also mix and match them.
In a different article, we'll look at how we can only make specific fields required or optional by leveraging some other utility types.
Thank you for reading, and let's connect!
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to subscribe to my email newsletter and connect on Facebook or Twitter